X-ray Absorption Edges
1a 2a 3b 4b 5b 6b 7b 8 1b 2b 3a 4a 5a 6a 7a 0
1 2
H He
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Li Be B C N O F Ne
11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18
Na Mg Al Si P S Cl Ar
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36
K Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr
37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54
Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In Sn Sb Te I Xe
55 56 57 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86
Cs Ba La Hf Ta W Re Os Ir Pt Au Hg Tl Pb Bi Po At Rn
87 88 89 104 105
Fr Ra Ac Rf Ha
Lanthanides 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71
Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu
Actinides 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103
Th Pa U Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf Es Fm Md No Lr
 Selecting any of the elements from the periodic table above will
retrieve ascii files containing tabulations of the characteristic x-ray
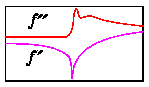
absorption edge energies, and of the anomalous scattering coefficients
f' and f" as a function of incident x-ray energy.
Selecting any of the elements from the periodic table above will
retrieve ascii files containing tabulations of the characteristic x-ray
absorption edge energies, and of the anomalous scattering coefficients
f' and f" as a function of incident x-ray energy.
 To generate a plot of selected scattering coefficients use the
forms interface to this data.
To generate a plot of selected scattering coefficients use the
forms interface to this data.
Where this data came from:
The scattering factor data files indexed through the table above were calculated
using the subroutine library by Brennan and Cowan (see
references).
The values for f' and f" are derived using the theoretical approximation
developed by Cromer and Liberman.
This theory gives accurate values far from an absorption edge but does not
account for the effects of neighboring atoms, which can be very substantial
near an absorption edge.
Before conducting an anomalous scattering experiment close to an
absorption edge it is therefore advisable to determine the actual scattering
behaviour of your sample (see theory v.
experiment).
Other periodic table interfaces to elemental properties:
 X-ray properties from W.H.McMaster's compilation of cross-sections
X-ray properties from W.H.McMaster's compilation of cross-sections
 The Pictorial Periodic Table
The Pictorial Periodic Table
 NMR periodic table
NMR periodic table
 WebElements home page
WebElements home page
 UBC (text-only interface)
UBC (text-only interface)
 YOGI (work in progress)
YOGI (work in progress)
 PeriodiCity
PeriodiCity
 X-ray Anomalous Scattering
X-ray Anomalous Scattering
Ethan A Merritt ©1996-2010/ merritt@u.washington.edu /
Biomolecular Structure Center at UW
 Selecting any of the elements from the periodic table above will
retrieve ascii files containing tabulations of the characteristic x-ray
absorption edge energies, and of the anomalous scattering coefficients
f' and f" as a function of incident x-ray energy.
Selecting any of the elements from the periodic table above will
retrieve ascii files containing tabulations of the characteristic x-ray
absorption edge energies, and of the anomalous scattering coefficients
f' and f" as a function of incident x-ray energy.
 X-ray properties from W.H.McMaster's compilation of cross-sections
X-ray properties from W.H.McMaster's compilation of cross-sections
 X-ray Anomalous Scattering
X-ray Anomalous Scattering